3 How to use the different tools
3.3 The ACT-Game
 3.3.3 Use in lessons
3.3.3 Use in lessons
The ACT - Game builds on the basic knowledge from the two booklets "Basic Human Needs" and "Strategies for Meeting Basic Needs".
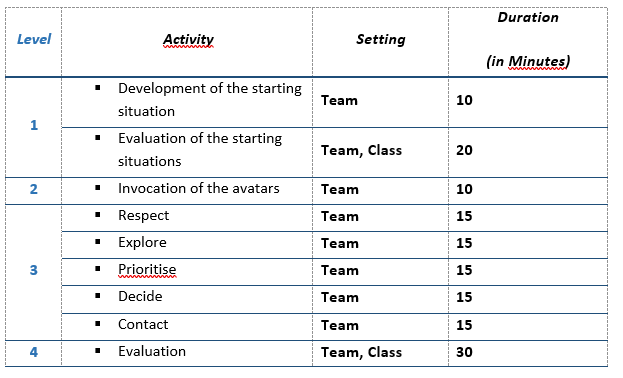
Overview of the contents and duration of the individual game levels:
Levels 1 and 2 can be completed in one school lesson.
Levels 3 and 4 should be played through in one piece, if possible, so that the players can get into the right mood and are not torn out of the flow of the game at an early stage. This requires at least one double lesson.
ACT-Phase
The ACT-Phase (Level 3) is the core of the game, as it provides a step-by-step introduction to participation in democratic decision-making processes. The following describes the basic ideas behind the individual actions.
Action 1 RESPECT
Recognise the different needs
In this first Action pupils shall empathise with the involved persons to acquire a more holistic view of the situation. This shall serve as a starting point for further actions. Very often, when people try to solve a problem, this step is skipped to save time. But this Action is very important to find a sustainable solution that all parties can agree to. With this exercise, pupils train to ...
- Empathise with other persons and their needs
- See a problem/situation from different perspectives
- Analyse a problem and get to the point
Action 2 – EXPLORE
Get more info
The next mistake people often make when they develop a strategy to solve a problem is to take too many facts as proven. This is why the next Action in the ACT game is to learn as much as possible about the problem. The advantages are that pupils ...
- Ask critical questions
- Learn about reliable sources
- Identify the most important information
The motto is: The more you know, the more opportunities you find.
Action 3 – PRIORISE
Spot your opportunities for action
Now we are moving towards the solution. To be able to prepare a good decision, you need criteria: What makes a good solution strategy? Although the criteria are quite simple, this important step is often not taken. However, the advantages are obvious: Decision-making is comprehensively prepared and goes more easily. In this Action the pupils learn …
- To distinguish a good from a bad strategy
- To consider the pros and cons of a solution
- To take the welfare and needs of others into consideration
- To explore alternative options
- To be aware of the multiplicity of opportunities
Action 4 – DECIDE
Find the best possible strategy
The way decisions are normally made is by voting. The solution that gets the most votes is chosen, regardless of how many dissenting votes are counted and usually without even hearing them. This often leads to solutions not being supported by all, perhaps passively or even actively sabotaged. Here, a way of decision-making is presented in which there are no losers, in which everyone can only win. It is called systemic consensing. By using this tool, pupils learn …
- To contribute to the best possible solution
- To regard the diversity of opinions as a resource
- To compromise
- To use resistance to bring about an improvement in the solution
Action 5 – CONTACT
Get in contact!
It is usually easy for us to get in touch with friends and like-minded people, but what about those in authority? Or with persons who disagree with us, who may even treat us unfairly or threaten us?
Following Marshall Rosenberg's four steps of non-violent communication, the pupils think about how they can communicate the solution they have found so that their counterparts can agree as much as possible. In doing so, they learn and train ...
- To see and recognise the needs of their conversation partner
- To formulate their own needs
- To distinguish between description, interpretation and evaluation
- How to approach someone with a different opinion
- To formulate a proposal in a way that the other person can feel understood
Even if the teams play the levels and actions of the ACT game independently, the teacher should be ready to support and answer questions at any time. More on this you find in the chapter "Possible obstacles and further options".